In recent decades, healthcare has undergone a remarkable evolution, transitioning from traditional, analog methods to a landscape increasingly defined by digital innovation. The integration of latest technologies has elevated this transformation, with Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerging as a major force revolutionizing the sector. AI's integration into healthcare has sparked a paradigm shift, reshaping how medical professionals diagnose, treat, and manage diseases. Its ability to analyze vast amounts of data, detect patterns, and generate actionable insights has unlocked unprecedented potential for improving patient outcomes, enhancing operational efficiency, and advancing medical research. Exploring the Landscape of AI in Healthcare
AI is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape, bringing new possibilities for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases.
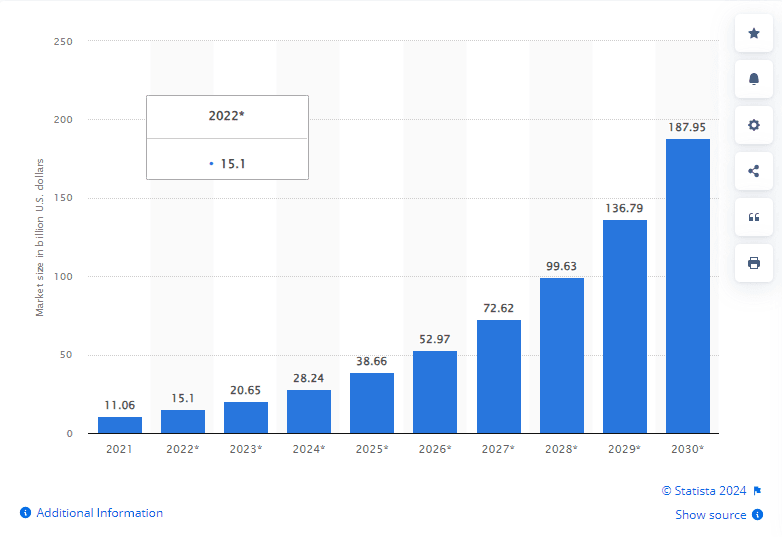
As per Statista, the AI Healthcare sector is estimated to reach a value of $187 billion by 2030. This substantial growth implies that significant transformations are expected to persist in the operations of medical providers, hospitals, pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms, and other players within the healthcare sector.
Improved Machine Learning (ML) algorithms, enhanced data accessibility, cost-effective hardware, and the widespread adoption of 5G technology have collectively propelled the expansion of AI within the healthcare sector, hastening the rate of innovation. These AI and ML advancements possess the capability to efficiently analyze vast quantities of health-related data, ranging from medical records and research studies to genetic data, at a pace significantly surpassing human capacity. As the popularity of health and fitness monitors grows and the use of health-tracking fitness apps becomes more widespread, individuals can now easily share real-time data sets with their healthcare providers to monitor their health status and receive alerts in case of any concerns. Furthermore, AI solutions, like big data applications, machine learning algorithms, and deep learning algorithms, offer opportunities to analyze vast data sets effectively, aiding in clinical decision-making and beyond. AI technology also holds promise in detecting and tracking infectious diseases such as COVID-19, tuberculosis, and malaria.
How is AI employed in the Healthcare Sector?
AI is increasingly becoming a transformative force in the healthcare sector, revolutionizing various aspects of medical practice, research, and administration. One prominent application is in medical diagnosis and imaging analysis. Advanced machine learning algorithms can analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with remarkable accuracy, aiding clinicians in detecting diseases like cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and neurological disorders at an early stage. Another crucial area where AI is making significant strides is in personalized medicine and treatment optimization. By analyzing vast amounts of patient data, including genetic information, medical history, and treatment outcomes, AI algorithms can predict individual patient responses to specific medications and therapies. This enables healthcare providers to tailor treatments to each patient's unique characteristics, maximizing efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
Moreover, AI is playing a pivotal role in streamlining healthcare operations and administrative tasks. Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms can automate medical transcription, coding, and documentation processes, reducing the burden on healthcare professionals and improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical records. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are also being deployed to provide patients with personalized health advice, schedule appointments, and answer inquiries, enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction.
Innovative Technologies Shaping Modern Healthcare Practices
In the healthcare domain, a range of technologies are currently utilized to elevate patient care, optimize operational processes, and enhance overall efficiency. Some examples of these technologies include:
Machine Learning (ML):
Machine Learning algorithms are revolutionizing medical imaging interpretation by automating tasks such as lesion detection, tumor segmentation, and organ localization. According to BIS Research, in 2022, the market for medical devices utilizing machine learning was assessed at $4,011.7 million. It is projected to surge to $35,458.2 million by 2032, demonstrating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 24.35% over the forecast span from 2022 to 2032. This technology enhances the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostic processes, helping radiologists identify abnormalities and make more informed treatment decisions. ML models analyze large datasets with the help of AI, comprising patient demographics, clinical variables, and health outcomes, to predict disease risks, patient outcomes, and healthcare utilization. These predictive insights enable early intervention, personalized treatment planning, and resource optimization within healthcare systems.
Example: One of Google's latest advancements in health-related research and efforts involves the enhancement of genomic discovery for optic nerve head morphology through machine learning models.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP technology automates the extraction and analysis of information from unstructured clinical notes, transcription reports, and medical literature. This facilitates accurate and efficient clinical documentation, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care and less on administrative tasks. AI collaborates with NLP algorithms to standardize and normalize healthcare terminology across disparate systems, fostering semantic interoperability and data exchange between healthcare organizations. This improves care coordination, facilitates clinical research, and enhances the accuracy of health information exchange.
Example: Med-PaLM 2 utilizes Google's LLMs, customized for the medical field, to provide more precise and secure responses to medical inquiries. Consequently, Med-PaLM 2 achieved a groundbreaking feat by becoming the inaugural LLM to exhibit an "expert" test-taker level performance on the MedQA dataset, styled after the US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) questions, achieving an accuracy of over 85%.
Data Analytics:
A marketsandmarkets.com 2022 report on Healthcare Analytics Market projected that the healthcare analytics market will reach 85.9 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 25.7%. Data analytics techniques include utilizing Electronic Health Records (EHRs), clinical databases, and medical literature to provide clinicians with evidence-based insights and decision support tools at the point of care. This empowers healthcare providers to deliver personalized treatment plans, adhere to clinical guidelines, and improve patient outcomes. Data analytics tools integrate with AI to aggregate and analyze population-level health data to identify high-risk patient cohorts, monitor health trends, and implement targeted interventions for disease prevention and health promotion. By proactively managing population health, healthcare organizations can mitigate disease burdens and reduce healthcare costs.
Example: AWS HealthLake is a service eligible for HIPAA that offers FHIR APIs, aiding healthcare and life sciences firms in securely storing, transforming, transacting, and analyzing health data within minutes. This facilitates a chronological perspective at both the patient and population levels.
AI for Disease Diagnosis
Image Recognition and Analysis:
AI-powered image recognition and analysis systems are trained to interpret medical images such as X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans. By leveraging deep learning algorithms, these systems can detect patterns and anomalies that may be indicative of diseases such as cancer, fractures, or abnormalities in organs.
For example, in radiology, AI algorithms can assist radiologists in detecting tumors or identifying areas of concern in medical images with high accuracy and efficiency. For example, using computer vision AI and image search functionalities, Google is in the process of creating a tool aimed at assisting people in thoroughly researching and identifying their skin, hair, and nail conditions. This tool accommodates hundreds of conditions, encompassing over 80% of those encountered in clinics and more than 90% of the most frequently searched conditions.
Early Disease Detection Algorithms:
Early detection of diseases significantly improves treatment outcomes and patient survival rates. AI algorithms can be trained on large datasets of patient information, including genetic data, medical imaging, and clinical records, to identify subtle signs and symptoms that may indicate the onset of diseases such as cancer, diabetes, or cardiovascular conditions. By flagging individuals at high risk of developing certain diseases, healthcare providers can intervene earlier with preventive measures or targeted screening programs.
For example, Siemens Healthineers, a company offering healthcare services, utilizes AI-driven predictive models to aid in the early detection of severe liver disease, potentially playing a vital role in the early diagnosis of liver cancer.
AI in Personalized Medicine
Analysis and Precision Medicine:
Genomic sequencing technologies generate vast amounts of genetic data, offering insights into an individual's susceptibility to certain diseases and their response to specific treatments. AI algorithms can analyze this genetic information to personalize medical interventions, such as selecting the most effective medications or designing tailored treatment plans based on an individual's genetic profile.
Drug Discovery and Development:
Traditional drug discovery processes are time-consuming and costly. AI accelerates drug discovery by analyzing biological data, identifying potential drug targets, and predicting the efficacy and safety of new compounds. Machine learning models can sift through large datasets of chemical compounds, biological interactions, and clinical trial results to identify promising drug candidates for further testing, significantly reducing the time and resources required for drug development. One illustration is that Pfizer researchers use computational tools such as MATLAB to support model-based drug development.
AI in Medical Imaging
Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging
AI algorithms enhance the accuracy and efficiency of radiological interpretations by assisting radiologists in detecting abnormalities and lesions in medical images. Deep learning models can analyze images from various modalities, including X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and mammograms, to aid in the diagnosis of conditions such as tumors, fractures, and vascular diseases. By highlighting areas of concern and prioritizing critical cases, AI helps radiologists make more timely and accurate diagnoses, leading to improved patient outcomes.
For example, Google offers AI technology in mammography to enhance breast cancer screening with artificial intelligence. This AI-driven system seamlessly integrates into breast cancer screening processes, aiding radiologists in detecting breast cancer at earlier stages and with greater consistency.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Surgical Planning
AR and VR technologies transform surgical planning and education by providing immersive, interactive experiences for healthcare professionals. Surgeons can use AR and VR simulations to visualize patient anatomy, practice surgical procedures, and plan complex interventions with greater precision and confidence. By integrating AI algorithms with AR and VR platforms, surgeons can access real-time guidance and decision support during surgeries, enhancing surgical outcomes and patient safety. For example, Vicarious Surgical has developed a robotic system that is operated through a VR headset, designed to offer both freedom of movement and precision during minimally invasive surgeries. This device interfaces with a VR headset and dynamically responds to the user's motions, granting an immersive view of the surgical site, akin to the surgeon being physically present.
Factors driving the Market Growth of AI in Health Care
In this section, we will find out the key factors that collectively drive the market growth of AI in healthcare, fostering innovation, improving patient care, and transforming the way healthcare services are delivered and managed.
Investment and Funding
Investment and funding in AI healthcare startups and research initiatives are crucial for the development and implementation of AI technologies. Investors recognize the potential for significant returns in this rapidly evolving sector, leading to increased capital allocation.
Industry Collaborations and Partnerships
Collaborations between healthcare institutions, technology companies, and research organizations facilitate the sharing of expertise, resources, and data. These partnerships accelerate the development of AI solutions, enabling faster deployment and adoption across various healthcare settings.
Improved Patient Outcomes
AI-driven technologies have the potential to enhance patient outcomes by enabling more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and proactive disease management. By leveraging large datasets and advanced analytics, AI systems can identify patterns and insights that may not be readily apparent to human practitioners, leading to better healthcare outcomes.
Cost Reduction
AI applications in healthcare can help streamline processes, optimize resource allocation, and reduce inefficiencies, ultimately leading to cost savings. By automating routine tasks, minimizing errors, and optimizing workflows, AI technologies contribute to more efficient healthcare delivery while reducing operational expenses.
Aging Population and Chronic Disease Burden
The aging population and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases place significant strain on healthcare systems worldwide. AI-powered solutions can help address these challenges by enabling early detection, preventive care strategies, and personalized interventions tailored to individual patient needs. By proactively managing chronic conditions and promoting healthy aging, AI contributes to better population health outcomes.
Major Setbacks of AI in Healthcare
While generative AI offers a transformative vision for healthcare, significant hurdles need to be addressed.
Data Privacy Concerns:
Generative AI in healthcare relies heavily on patient data for training models. This raises significant concerns about data privacy and security. Patient data is highly sensitive, and any breach or misuse could lead to severe consequences for individuals and institutions alike. Ensuring robust data protection mechanisms and adhering to strict privacy regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) are crucial.
Bias and Lack of Diversity in Data:
Generative AI models are only as good as the data they're trained on. If the training data is biased or lacks diversity, the generated outputs may also reflect these biases. In healthcare, biased AI could lead to inaccurate diagnoses, treatment recommendations, or disparities in healthcare delivery. Efforts must be made to address bias in training data and ensure diversity to improve the fairness and effectiveness of generative AI systems.
Potential for Malicious Use:
Like any other technology, generative AI in healthcare can be exploited for malicious purposes. For instance, adversaries could manipulate AI-generated medical images or records to deceive healthcare providers or tamper with patient data for fraudulent activities. Safeguards such as robust authentication, encryption, and monitoring systems are necessary to mitigate the risks of malicious use.
Complexity in Integration with Existing Systems:
Integrating generative AI into existing healthcare systems can be complex and challenging. Healthcare organizations often have diverse IT infrastructures, interoperability issues, and regulatory constraints. Deploying generative AI solutions seamlessly within this complex ecosystem requires careful planning, collaboration, and investment in IT infrastructure and personnel training.
Ethical Considerations of AI in Healthcare Sector
The integration of AI in the healthcare sector presents numerous ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed to ensure patient well-being, privacy, equity, and trust. Here are some key ethical considerations:
Patient Privacy and Data Security:
AI systems in healthcare often rely on vast amounts of patient data for training and operation. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is paramount. Healthcare organizations must implement robust data protection measures, including encryption, access controls, and anonymization techniques, to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive patient information.
Transparency and Accountability:
AI algorithms can be complex and opaque, making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions. There is a need for transparency in AI systems to enable clinicians and patients to understand the rationale behind AI-driven diagnoses and treatment recommendations. Moreover, clear lines of accountability should be established to attribute responsibility in cases of AI errors or biases.
Bias and Fairness:
AI algorithms are susceptible to biases inherent in the data used to train them, which can result in discriminatory outcomes, particularly in healthcare settings where decisions impact patient lives. Efforts should be made to identify and mitigate biases in AI algorithms to ensure fairness and equity in healthcare delivery.
Informed Consent and Autonomy:
Patients should be adequately informed about the use of AI technologies in their healthcare and have the opportunity to consent to or opt out of AI-driven interventions. Additionally, AI should not undermine patient autonomy or replace human judgment, but rather complement clinical decision-making processes.
Emerging Trends of Generative AI in Healthcare
Integration of AI with Internet of Medical Things (IoMT):
According to Fortune Business Insights, the market size of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) was USD 41.17 billion in 2020. It is forecasted to rise from USD 30.79 billion in 2021 to USD 187.60 billion by 2028, marking a CAGR of 29.5% during the period from 2021 to 2028. The global effect of COVID-19 has been remarkable and significant, with the Internet of Medical Things experiencing heightened demand across all regions during the pandemic.
AI algorithms integrated with IoMT devices are enabling real-time monitoring of patient vital signs and health metrics, as well as predictive analytics to identify potential health issues before they escalate. IoMT devices equipped with AI capabilities are facilitating remote patient care by enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients' conditions from a distance, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Advancements in Explainable AI (XAI) for Healthcare
XAI techniques are being developed to provide healthcare professionals with explanations and insights into the decisions made by AI algorithms, enhancing trust and understanding of AI-driven recommendations for diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient management. XAI is playing a crucial role in ensuring regulatory compliance in healthcare AI systems by providing transparent explanations of how algorithms reach their conclusions, thereby addressing concerns related to accountability and ethical considerations.
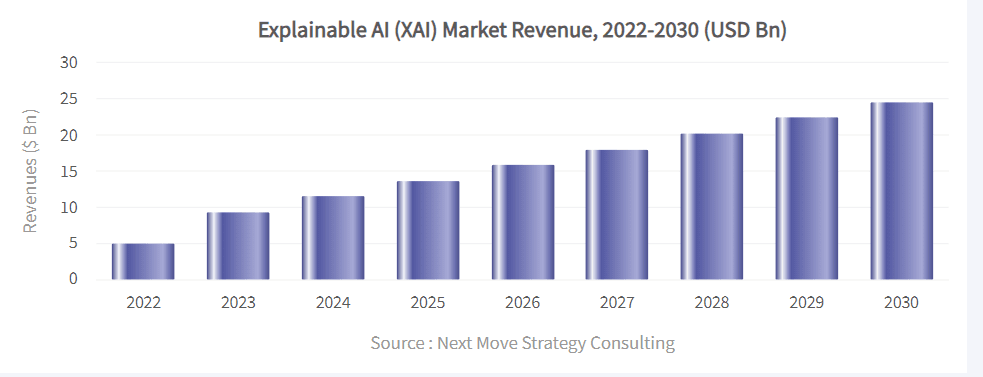
As per the Next Move study, the worldwide market for explainable AI (XAI) was valued at USD 5.10 billion in 2022, and projections suggest it will escalate to USD 24.58 billion by 2030, demonstrating a CAGR of 21.5% from 2023 to 2030.
XAI methods are facilitating the clinical validation and adoption of AI technologies in healthcare by enabling healthcare professionals to interpret and validate the results produced by AI algorithms, leading to increased acceptance and integration of AI into clinical practice.
Global Collaborations and Initiatives for AI in Healthcare
In recent years, there has been a surge in global collaborations and initiatives aimed at harnessing the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare. Organizations, governments, and research institutions worldwide are recognizing the transformative power of AI in revolutionizing healthcare delivery, from diagnostics to personalized treatment plans. One prominent example of international collaboration is the World Health Organization's (WHO) efforts to establish guidelines and frameworks for the ethical implementation of AI in healthcare, ensuring equitable access and patient privacy protection across borders. Additionally, multinational partnerships between tech giants, healthcare providers, and academic institutions have emerged to pool resources and expertise in developing AI-driven solutions for various healthcare challenges, such as disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and patient management.
AI's Next Steps in Healthcare and Beyond
The future of AI in healthcare holds immense promise. It is poised to revolutionize every aspect of the industry, from diagnosis to treatment and beyond. With the exponential growth of medical data, AI algorithms will play a pivotal role in analyzing vast amounts of information, enabling more accurate and timely diagnoses. Machine learning models will continually improve, learning from real-world data to enhance their diagnostic capabilities, potentially even predicting diseases before symptoms manifest. AI-driven tools will streamline administrative tasks, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care. Virtual health assistants powered by AI will provide personalized guidance and support to patients, promoting healthier lifestyles and better adherence to treatment plans. Moreover, AI will facilitate precision medicine, tailoring therapies to individual genetic profiles and health histories, leading to more effective treatments with fewer side effects. However, as AI becomes more integrated into healthcare systems, ensuring privacy, security, and ethical use of patient data will be paramount. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, data scientists, policymakers, and ethicists will be essential in harnessing the full potential of AI while safeguarding patient well-being and trust in the healthcare system.
Transforming Healthcare with Next-Gen Solutions
SoluteLabs holds a crucial position in advancing the healthcare sector with its inventive solutions and technologies. Its impact spans various areas, including the development of software platforms and the crafting of customized hardware solutions to meet healthcare demands. It bridges the gap between technology and healthcare by leveraging advancements such as mobile apps, wearables, and data analytics. Don't hesitate any further. If you're enthusiastic about beginning this transformative journey or require updates to your specific application, get in touch with us now. Let's navigate towards a future that is more agile, responsive, and prosperous together!