Healthcare payers are being asked to operate at a speed and level of transparency their legacy systems were never designed for. Claims volumes continue to rise, member expectations now mirror real-time financial services, and administrative costs remain under constant pressure. Yet, many payer organizations still rely on manual workflows to process claims, payments, and authorizations, creating delays that are no longer defensible. Studies reveal that over 53% of healthcare organizations have automated their payment workflows.
It is no longer just a matter of efficiency for US healthcare payers but that of regulation as well. The CMS-0057-F Interoperability and Prior Authorization Final Rule will be fully effective in 2026, and, accordingly, payers will be under a legal obligation to enable real-time data exchange, FHIR R4/R5 APIs, and considerably shorter prior authorization decision timeframes. Payers' monolithic core systems, which were put together over 30 years ago and have not been designed for this high level of interoperability, auditability, or responsiveness, are simply not up to the task. The administrative status quo is at an end.
In this blog, we will look at how technology is quietly changing the way healthcare payer operations work. Instead of focusing on buzzwords, the discussion centers on practical shifts, where automation helps, where data actually makes a difference, and how payers are gradually moving away from manual work toward systems that are easier to manage day to day.
Why Traditional Healthcare Payer Systems Fall Short Today?
Most payer teams already know something feels off. Work takes longer than it should, questions keep coming back, and small issues turn into bigger ones. A lot of that comes down to how older systems behave under modern pressure. Here are some of the challenges that a traditional healthcare payer system faces:
Limited Cost Transparency
Members often don’t really know what they’re paying for. They see numbers, but not explanations. In day-to-day healthcare payer services, this lack of clarity leads to confusion, follow-ups, and a general feeling that things are harder than they need to be.
Slow Financial Workflows
Claims and payments still pass through too many hands. Reviews take time. Corrections take even longer. When payer solutions in healthcare rely heavily on manual steps, teams end up reacting all day instead of getting ahead of the work.
Resource and Infrastructure Constraints
Older platforms were built to stay stable, not flexible. Adding a new tool or changing a process can feel risky. Without a real healthcare payer solution modernization, even simple upgrades turn into long projects, and innovation slows down.
Rising Healthcare Costs
Expenses rise every year, but older systems don’t always explain why. Data arrives late. Insights come after decisions are already made. That leaves payers responding to cost increases instead of managing them early.
Core Technologies Revolutionizing Payers Operations
Technology in payer organizations doesn’t always arrive as a big transformation. Most of the time, it shows up quietly. A task that used to take hours gets done faster. A question gets answered without multiple systems involved. Over time, these small shifts start to change how work actually feels day to day.
- Automation and AI-Driven Processes: A lot of payer work used to be repetitive, like checking claims, matching data, and routing approvals. Automation takes those pieces off people’s plates. As part of healthcare payer digital transformations, AI helps handle routine work so teams can focus on the situations that really need human attention.
- FHIR-Native Architectures: In order to comply with the 2026 Payer-to-Payer Data Exchange requirements, various teams are developing single data layers that can convert old claims data into standard USCDI (United States Core Data for Interoperability) elements instantly. As a result, payers are able to satisfy the requirements of interoperability in a way that does not harm their central administrative platforms and, at the same time, guarantee traceability, audit readiness, and uniform data exchange with all their partners.
- Generative AI and Data Insights: Data has always been present, but the real trick has been making it useful. Generative AI can comb through vast amounts of data, identifying trends and even distilling key points without the need for tedious manual analysis. This makes insights not just easier to find, but also quicker to act upon.
- Cloud Platforms and Modern Data Foundations: Cloud platforms stand out because they can scale up as needed and play nicely with other tools. For many businesses, this offers a sensible path to modernizing their old payment systems incrementally, avoiding the need for a complete system replacement.
- Digital Payments and Revenue Flow: The traditional payments have evolved; they're no longer just a back-office function. Digital solutions now handle premiums, reimbursements, and adjustments with greater efficiency. This shift leads to fewer bottlenecks and simplifies tracking financial flows, benefiting both internal teams and external partners.
- Member Interaction Tools: Tools that support member interaction have also changed. Member portals, mobile apps, and intuitive self-service options have set a new standard for convenience. These tools empower individuals to manage their coverage, monitor claims, and find answers without the usual delays.
Also Read: How AI Agents Are Redefining Healthcare and Patient Care?
Key Benefits of Technology in Healthcare Payer Solutions
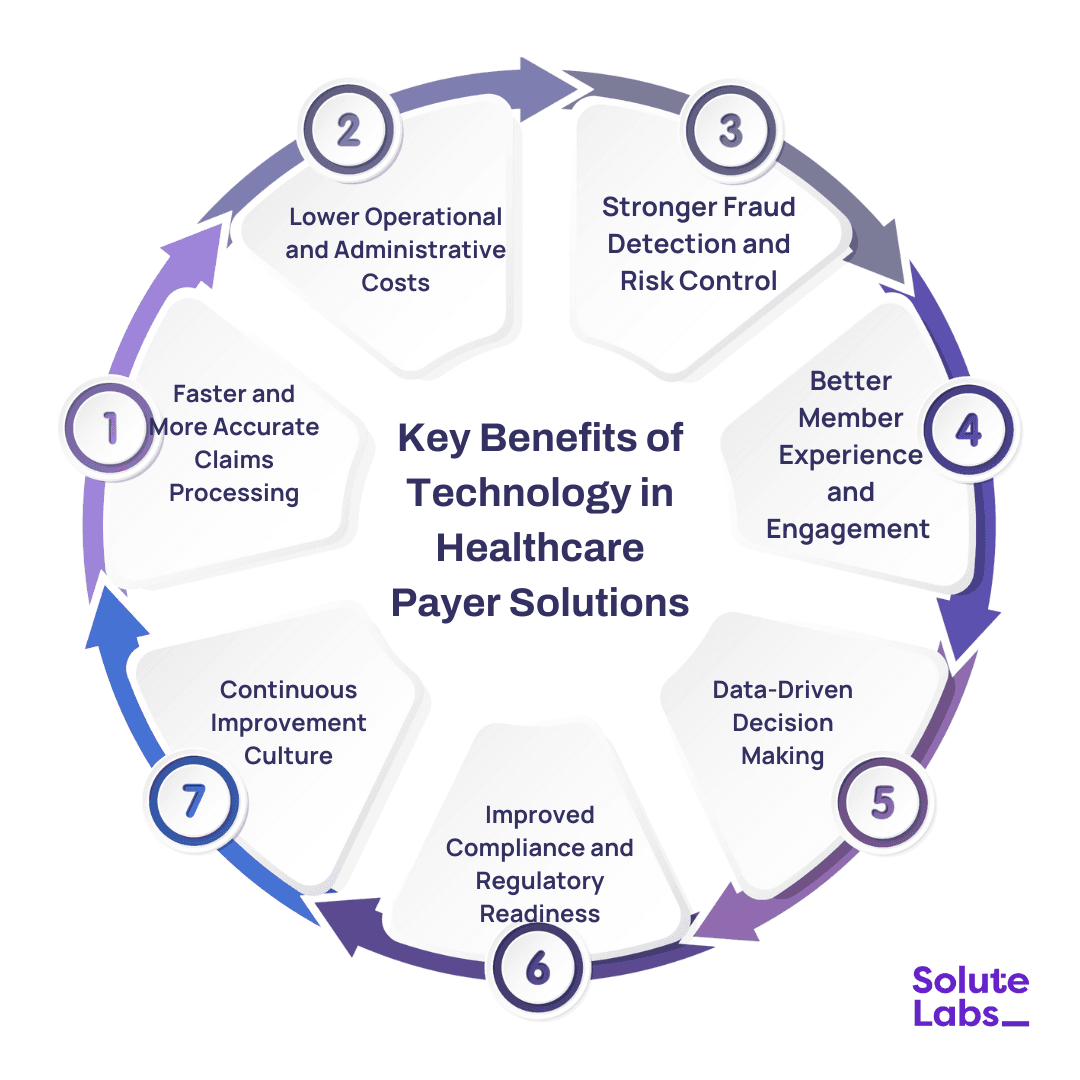
When technology starts fitting into payer workflows the right way, the impact is felt quickly. Work moves faster, fewer issues pile up, and members notice that things feel easier to deal with. Over time, these changes quietly improve both efficiency and trust. Mentioned below are some of the key benefits of utilizing AI in healthcare payer solutions:
Faster and More Accurate Claims Processing
Claims no longer need endless manual reviews. Automation helps catch errors early and move approvals along. This allows payer solutions in healthcare to reduce delays and avoid unnecessary back-and-forth with providers.
Lower Operational and Administrative Costs
Paperwork, rework, and manual checks add up fast. Digital tools reduce that load without disrupting daily operations. Many digital healthcare payers see cost savings simply by removing steps that no longer serve a purpose.
Stronger Fraud Detection and Risk Control
Fraud rarely shows up in obvious ways. Technology helps spot unusual patterns before they turn into real losses. This gives payer teams more confidence in how risks are identified and managed.
Better Member Experience and Engagement
Members appreciate simple answers delivered promptly. Digital access to claims information, coverage specifics, and real-time updates streamlines interactions, minimizing frustration. This approach, over time, lessens the volume of support requests and fosters trust.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Teams can move beyond guesswork by gaining visibility into claims, costs, and usage patterns. Access to dependable data empowers leaders to anticipate needs and respond with greater precision.
Improved Compliance and Regulatory Readiness
Keeping pace with frequently changing regulations can be a challenge when done manually. When healthcare payers design digital payment solutions with compliance as a priority, documentation remains tidy, and preparing for audits becomes significantly less burdensome.
Real-World Use Cases of Technology in Healthcare Payer Solutions
Technology in payer organizations is not always glamorous. Most of the time, it's the small improvements that make work easier. Here are some examples:
- AI-Powered Claims Automation: Claims processing was a slow and tedious process due to the manual work involved. LLM-based agents have taken over clinical intent reviews, which has led to an 80%reduction in manual prior, auth interventions. Moreover, they are capable of maintaining HIPAA-compliant audit trails.
- Predictive Risk Stratification for Value-Based Care & SDOH: Advanced machine learning models serve as early warning systems that help payers spot high-risk members long before they have avoidable ER visits or hospitalizations. These systems achieve this by fusing claims and utilization data with Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) like housing stability and transportation access. As a result, they enable care management to be not only timely but also proactive. The outcome for Value-Based Care programs is that it becomes possible to allocate resources more efficiently and achieve quantifiable reductions in Medical Loss Ratio (MLR).
- Fraud, Waste, and Abuse Detection: Fraud isn't always obvious. Modern analytics can quickly pinpoint duplicates, overcharges, or other irregularities.
- Personalized Health Plan Recommendations: Members are not identical. By examining coverage history and usage patterns, the system recommends plans that truly meet the individual's needs. It is like having a guide instead of a confusing stack of options.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants for Member Support: Nobody enjoys being put on hold. Virtual assistants offer immediate answers to questions about claims, benefits, and coverage.
- Digital Payment and Billing Solutions: Bills and payments can be complicated. Digital transformation in healthcare payers simplify the management of premiums, reimbursements, and transactions. This clarity benefits both members and staff.
Future Trends in Payer Technology Innovation
Healthcare payer technology is shifting beyond incremental efficiency gains toward systems that actively anticipate operational and member needs. Advances in predictive analytics, AI, and generative technologies are enabling payers to surface risks earlier, streamline decision-making, and act on data before costs escalate.
At the same time, digital platforms are reshaping how payers engage members. Self-service portals, mobile apps, and AI-driven assistants are reducing friction, improving transparency, and minimizing avoidable support interactions. The broader shift is clear: payer organizations are moving from reactive operations toward proactive, data-driven models that are better aligned with regulatory demands and member expectations.
The Bottom Line
Things are changing fast in healthcare payer work. Claims move quicker, mistakes happen less, and people can focus on the stuff that actually matters. It’s the little improvements, the small fixes, that make a big difference day to day.
Systems are getting smarter, too. AI, analytics, cloud platforms, they don’t just speed things up, they start to predict problems, help with decisions, and make member interactions easier. Apps, portals, and virtual helpers mean members can get answers without calling anyone. It feels simpler, less stressful, and just smoother.
At SoluteLabs, we help payers bring these innovations into action. We work with payers to bring in healthcare payer digital solutions, fix old systems, and make operations easier. If you want your team to work smarter and members to be happier, just contact us today.
