It is imperative that you begin your HIPAA compliance process if you are any kind of healthcare organization that deals with patient data. HIPAA provides the standards for maintaining patient information confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Compliance will not only keep you safe from huge fines but also gain the trust of your patients by demonstrating how serious you are about their privacy protection.
This article goes in-depth on the most crucial HIPAA compliance requirements, best practices, and actions your organization needs to take to create secure healthcare software and maintain continued compliance. If your organization is a small clinic or an enterprise, knowing these basics gets you off on the right foot.
Why HIPAA Compliance is Important?
In the healthcare sector, safeguarding confidential patient data is essential, both ethically and legally. HIPAA compliance services are an organized method of safeguarding Protected Health Information (PHI), keeping your organization up to date with strict federal regulations.
HIPAA compliance requirements and understanding are not a choice; noncompliance will cost millions of dollars in penalties, lawsuits, and irrecoverable patient trust. Besides penalties, noncompliance also violates reputations that have the potential to destroy business relationships and growth.
Healthcare cyber attacks on data are getting more sophisticated and abundant, and compliance with HIPAA has never been more important. With every step you take to implement HIPAA policies, you become more breach-resistant. HIPAA compliance best practices are not box-checking exercises; they are about instilling a culture of security essential to quality patient care.
This guide will walk you through critical steps to HIPAA compliance, offer real-world advice on HIPAA compliant healthcare technology & offer an implementation guide to help you design and maintain a secure, compliant setting for your organization.
Also Read: How to Develop a HIPAA Compliant Mobile Application - Entrepreneur’s Guide
Understanding HIPAA Compliance Requirements
HIPAA compliance safeguards sensitive patient information at the national level. It is primarily applicable to covered entities like healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses that deal with Protected Health Information (PHI).
HIPAA Key Rules
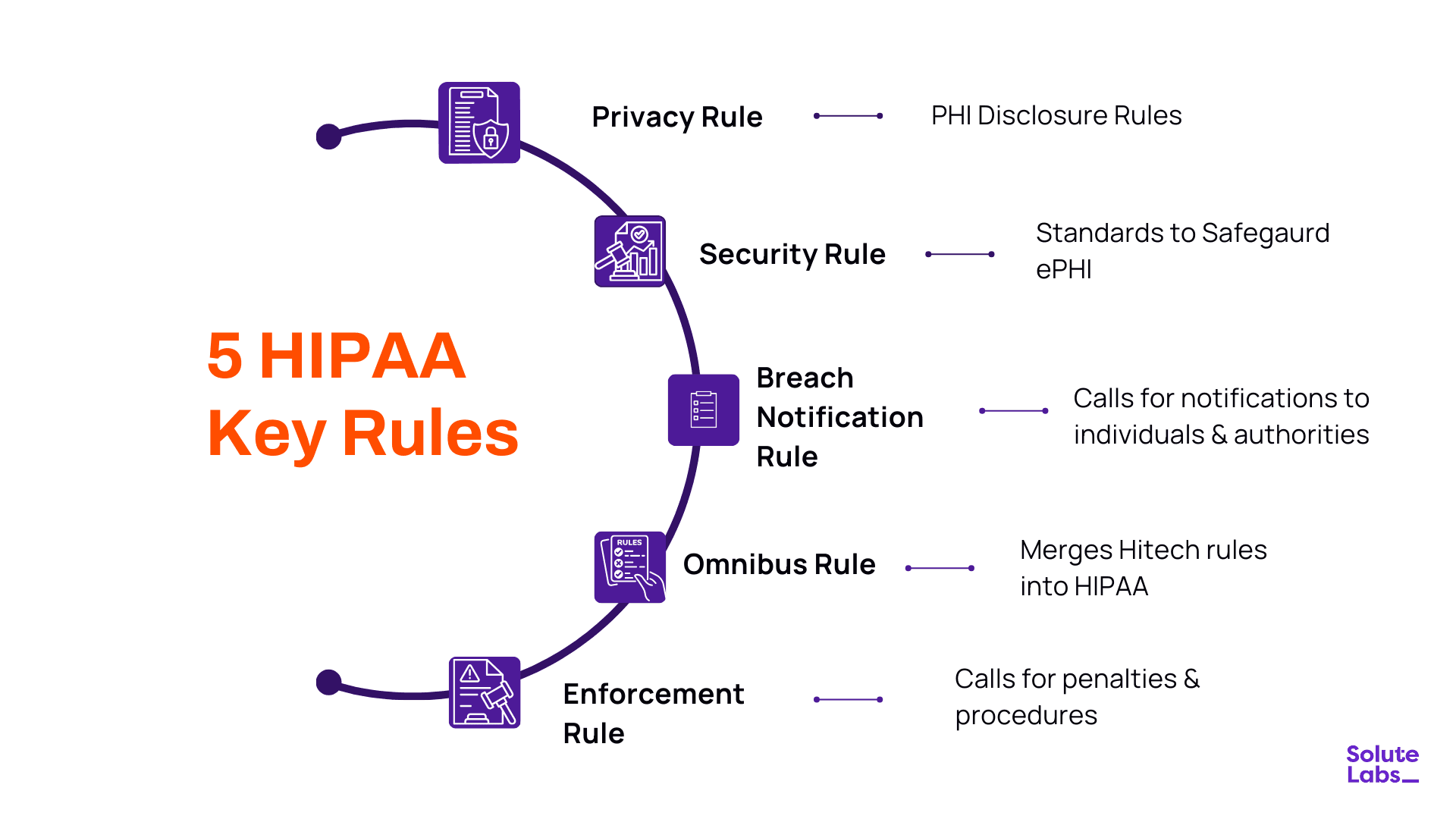
- Privacy Rule: Regulates the use and disclosure of PHI and provides patients with rights to access and own their information.
- Security Rule: Mandates administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to safeguard electronic PHI (ePHI).
- Breach Notification Rule: Calls for notification to individuals and authorities when breaches occur.
- Omnibus Rule: Increases enforcement & applies requirements to business associates.
- Enforcement Rule: Calls for penalties & procedures in case of non-compliance.
2025 rules also emphasize the necessity of mandated multi-factor authentication (MFA) & more stringent enforcement guidelines, keeping the bar high on security. Being compliant with these HIPAA requirements not only guarantees regulatory compliance but also builds trust with secure strength.
Major Steps to HIPAA Compliance
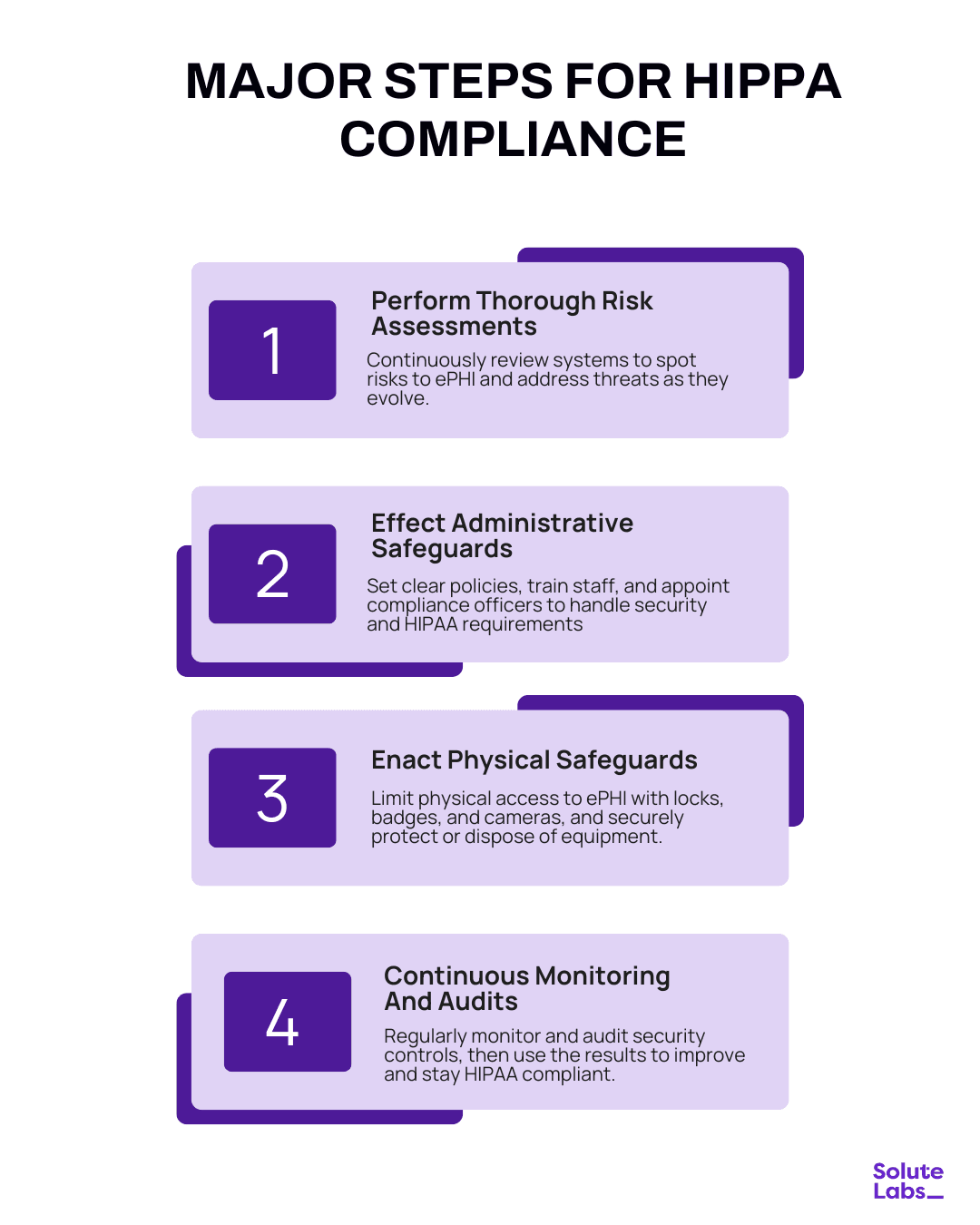
Achieving HIPAA compliance is a matter of careful rollout of administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect sensitive health data. The following are the key steps to take:
- Perform Thorough Risk Assessments: Evaluate the processes and systems within your organization, identifying risks and potential threats to electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). Continuous risk analysis enables prioritizing remediation against changing threats.
- Effect Administrative Safeguards: Enforce and implement procedures and policies to govern staff activity, training, and incident response. Appoint HIPAA compliance officers and train your workforce to implement best practices in the detection and reporting of security breaches.
- Enact Physical Safeguards: Restrict physical access to facilities and equipment that store or handle ePHI. Enact use controls such as locks, badges, and video cameras. Protect desktops & dispose of equipment securely to avoid data compromise.
- Continuous Monitoring And Audits: Continuously monitor security controls and audit compliance on a regular basis. Use audit findings to enhance controls, mitigate risks, and attain HIPAA compliance standards.
Developing a HIPAA Compliant Database
A HIPAA compliant database plays an essential role in the protection of sensitive health data. Data that is encrypted both in transit and at rest stops unauthorized use or access, role-based access controls restrict what permitted staff can read or update patient data, and all database activity is logged, allowing suspicious behavior to be identified. Resilient backup and disaster recovery procedures are also needed to help guarantee data availability and integrity, even in the case of an occurrence.
When choosing storage, cloud computing is more flexible and easier to upgrade, but it also has to meet stringent HIPAA requirements, including the use of Business Associate Agreements (BAA) and encryption of communications. On-premises storage offers more management control but requires careful physical and network security administration.
Secure setup and continuous vulnerability management, i.e., regular patching and penetration testing are critical to maintaining compliance. SoluteLabs helps build HIPAA compliant healthcare software, guiding you every step of the way from database security to HIPAA compliant software development with battle-tested best practices.
HIPAA Compliant Software Development
It starts by following secure development methods and keeping the patient information safe. Begin by conducting a HIPAA risk assessment to identify areas of vulnerability in your processes and electronic infrastructure. Apply threat modeling to uncover what data flow exists within your software and where risks can occur so that you can establish sound security protocols to develop HIPAA compliant software from the outset.
Key development steps are:
- Implement robust encryption for PHI, both stored and in transit.
- Use role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication to limit the release of data.
- Validation of user input & sanitization of output for preventing security attacks.
- Keeping comprehensive activity logs and audit trails.
- Compliance certification, through regular third-party audits, guarantees that the software is HIPAA compliance standard compliant. Having HIPAA compliance services as part of your Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) guarantees that every phase, from planning to deployment, is in accordance with the regulations.
Best Practices for HIPAA Compliance
A proactive approach is fundamental for organizations aiming to achieve HIPAA compliance and reduce risks. Consistently following best practices ensures sensitive health data is safeguarded, staff are well prepared, and regulatory standards are met, all key to patient trust and business credibility.
Data Encryption and Secure Communication
Use robust encryption methods for health information at all times, whether data is in storage, transit, or backup. Always implement HTTPS/SSL for every data transfer through your healthcare applications, keeping communications confidential.
Vendor Management and Access Control
Work only with vendors who sign Business Associate Agreements (BAA), ensuring they meet compliance standards. Enforce the principle of least privilege, granting staff only the minimum access needed for their job.
Continuous Training and Audit Trails
Run staff training regularly so everyone understands HIPAA requirements and incident response. Prepare breach notice protocols, enabling rapid action if needed. Maintain detailed records of compliance activities, from risk assessments to incident reports—documenting every effort ensures clear evidence of HIPAA compliance services and requirements.
HIPAA Compliance Checklist Explaining What Organizations Need To Do
A HIPAA checklist puts your company ready and secure with all of the essential requirements constantly met. Here is what should be included in your checklist:
- Perform risk assessments on a regular basis to identify vulnerabilities in your processes and systems.
- Provide regular employee training so that all employees are current with the standards and practices needed to ensure HIPAA compliance and best practices in data security.
- Document all policies, procedures, and compliance; tidy records are quicker for audits and accountability.
- Encrypt patient data, both in storage and when transporting data, to minimize exposure.
- Develop an explicit incident and breach response plan to provide for speedy reporting and remediation.
HIPAA Compliance Software: Cost & Considerations
HIPAA compliance software prices can range quite extensively, but knowing the key determinants allows you to pick the ideal fit for your organization.
- Small clinics will pay $30–$100 per month for basic compliance software.
- Big enterprises will anticipate pricing of $1,000–$4,300 per month or more for feature-rich, scalable solutions with advanced integrations and audit features.
- Pricing is determined by database size, complexity of required integrations, rate of regulatory audits & degree of advanced reporting needed.
- Cloud-based HIPAA compliance software has lower initial costs, automated maintenance, and simpler scaling, which appeal to cost-saving teams. On-premise software may be more expensive in terms of hardware, labor-intensive maintenance & IT support, but it might be the option for data sovereignty or customization needs in organizations.
- Purchasing a HIPAA compliance service ensures that your software choice aligns with your operations budget and risk profile.
HIPAA Compliance Risks & How to Mitigate Them
Typical HIPAA compliance risks include data breaches, insider threats, weak password practices, inadequate training of staff, and insecure devices. These equate to unauthorized viewing or disclosure of patient information and result in significant financial and reputational loss.
The risks are mitigated by the organization through:
- Applying multi-factor authentication and secure password policies to all user accounts.
- Limit user permissions with least privilege access controls.
- Offer frequent employee education on HIPAA policies and secure management of PHI.
- Encrypt sensitive data in databases and when transferring.
- Continuously monitor systems & keep detailed audit trails to identify and react to suspicious activity immediately.
How SoluteLabs Assists With HIIPA Compliance?
SoluteLabs simplifies HIPAA and GDPR compliance with expert consulting, risk assessment, and custom software development specifically for healthcare organizations. From secure databases and mobile apps to solid APIs, our experts ensure that each solution is HIPAA-compliant at every step.
We walk you through risk analysis, deploy trusted data protection protocols & keep your teams audit-ready, so you can be sure your patient data is always safe and compliant.
Conclusion
HIPAA compliance protects patient health data & establishes confidence in your healthcare organization. Be a HIPAA compliance leader, not only to protect sensitive data but also to prevent expensive fines and loss of reputation. Healthcare organizations need to have enforceable compliance controls and make an investment in secure software products that are coded to maintain regulatory standards.
Having custom software healthtech certified technology professionals like SoluteLabs on board ensures that your healthcare software's HIPAA compliance is both feasible and long-term.
