The marine industry, responsible for over 80% of global trade, is seeing significant change driven by AI technologies. According to a report by Lloyd's Register, the maritime AI market has been growing rapidly, reaching a value of $4.13 billion in 2024. This marks a nearly threefold increase from the previous year, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23% projected for the next five years. This growth reflects a broader trend of modernization, where digital transformation is paving the way for smarter, more efficient operations across the industry.
AI is driving real change in areas such as navigation, predictive maintenance, and port operations. Autonomous vessels are becoming a reality, while AI systems optimize logistics and safety protocols, making maritime operations faster and more sustainable. With these advancements, businesses can reduce costs, enhance reliability, and deliver higher-quality services, positioning themselves as leaders in an evolving market.
As AI continues to revolutionize the industry, stakeholders must stay informed and embrace these changes. In this blog, we will explore the role of AI in reshaping the marine industry, focusing on how companies can use AI-powered marine solutions for improved operational efficiency, sustainability, and competitiveness.
Overview of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming industries, including the shipping sector. AI involves creating systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as problem-solving, decision-making, and language understanding. Machine Learning, a branch of AI, focuses on enabling machines to learn from data, adapt, and improve without being directly programmed.
In the shipping industry, AI and ML are making a significant impact by enhancing operations and increasing efficiency. These technologies allow ships to make smarter decisions in real-time, such as adjusting routes based on changing weather conditions or predicting when maintenance is needed. Machine learning in the shipping industry plays a key role in analyzing vast amounts of data, helping companies optimize fuel consumption, improve safety, and reduce operational costs.
As these technologies continue to change, they offer the potential to transform the entire shipping process, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable for businesses in the maritime sector.
Differentiating AI from Traditional Software
While traditional software operates based on pre-programmed rules and logic, AI systems, particularly those employing machine learning, can adapt and improve their performance over time. Key differences in the maritime context include:
Adaptability:
AI systems can adjust their behavior based on new data, whereas traditional software remains static unless manually updated.
Handling Complexity:
AI can process and make decisions based on vast amounts of unstructured data, a task that would be impractical for traditional rule-based systems.
Predictive Capabilities:
Unlike traditional software, AI can make predictions and recommendations based on complex pattern recognition.
Autonomous Decision-Making:
Advanced AI systems can make decisions independently, a crucial feature for autonomous vessel operations.
AI’s Application to the Maritime Industry
Autonomous Vessels and Navigation Systems in Marine Industry
Autonomous vessels, powered by sophisticated AI algorithms, are pioneering the maritime industry. These ships utilize a complex network of sensors, cameras, radar systems, and AI-driven decision-making processes to navigate without or with minimal human intervention. The development of autonomous vessels in the marine industry is progressing through various levels of autonomy, from digitalization in the maritime industry, partial automation, to fully autonomous operations.
- Sensor Fusion and Data Integration: Autonomous vessels employ multiple sensor types, including LiDAR, radar, AIS (Automatic Identification System), and high-resolution cameras. AI algorithms fuse data from these diverse sources to create a comprehensive situational awareness model.
- Machine Learning for Navigation: Deep learning models, trained on vast datasets of maritime traffic patterns, weather conditions, and navigational hazards, enable autonomous vessels to make real-time decisions regarding course adjustments, speed optimization, and collision avoidance.
- Dynamic Positioning Systems: AI-enhanced dynamic positioning systems maintain vessel position and heading with unprecedented precision, even in challenging water conditions, by continuously analyzing environmental forces and adjusting propulsion systems accordingly.
- Advanced Navigation Systems: AI integration has accelerated the evolution of navigation systems in the maritime sector, resulting in more precise, effective, and safe voyages.
- Intelligent Electronic Chart Display and Information System (ECDIS): AI-powered ECDIS platforms like Simrad offer enhanced route planning capabilities, incorporating real-time data on weather patterns, ocean currents, and traffic density to suggest optimal routes that minimize fuel consumption and maximize safety.
- Augmented reality (AR) Navigation: AR systems, which are controlled by AI algorithms, add important navigational information on top of the bridge's view of the navigation systems. This gives marine officers easy-to-understand visual cues for navigation hazards, nearby ships, and the best routes to take.
- Adaptive Autopilot Systems: Machine learning algorithms continuously refine autopilot performance, adapting to changing sea conditions and vessel characteristics to maintain optimal course and speed with minimal human intervention.
- Collision Avoidance Systems: In the marine industry, advanced AI models look at complicated traffic situations in real time, predicting possible collision risks and making avoidance maneuvers on their own when needed, all while following COLREGS (International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea).
Predictive Maintenance for Ships and Equipment
AI-driven condition monitoring systems are fundamentally supportive of predictive maintenance in the maritime sector. These sophisticated AI in shipping systems employ a network of sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to collect real-time data from various ship components and equipment continuously. Key elements include:
- Vibration Analysis: Advanced accelerometers and vibration sensors monitor the mechanical health of rotating equipment such as propulsion systems, generators, and pumps.
- Acoustic Emissions Monitoring: Ultrasonic sensors detect high-frequency sound waves emitted by equipment, indicating potential issues like leaks or structural defects.
- Thermography: Infrared cameras and thermal sensors track temperature variations in electrical systems and machinery, identifying hotspots that may indicate impending failures.
- Fatigue and Stress Prediction: AI models simulate and predict structural stress and fatigue based on operational data, environmental conditions, and historical performance.
- Oil Analysis: In-line oil sensors perform real-time analysis of lubricant conditions, detecting contaminants and wear particles that signal equipment degradation.
- Performance Monitoring: AI algorithms analyze operational data to identify deviations from optimal performance parameters, indicating potential maintenance needs.
Integration with Vessel Management Software
Predictive maintenance systems are increasingly integrated with comprehensive vessel management software, creating a holistic approach to ship operations. This integration enables:
- Automated work order generation based on AI-predicted maintenance needs.
- Optimization of maintenance schedules in conjunction with voyage planning and port calls.
- Real-time updates to maintenance budgets and inventory management systems.
- Enhanced decision support for fleet managers and technical superintendents.
AI-Powered Maintenance Planning and Optimization
AI algorithms play a crucial role in optimizing maintenance planning and execution:
- Maintenance Prioritization: Machine learning models assess the criticality of predicted maintenance tasks, considering factors such as equipment importance, failure consequences, and operational impact.
- Resource Allocation: AI optimizes the allocation of maintenance resources, including spare parts, personnel, and time, based on predicted needs and operational constraints.
- Predictive Spare Parts Management: AI algorithms forecast spare parts requirements, optimizing inventory levels and reducing the risk of stockouts or excess inventory.
- Maintenance Route Optimization: For autonomous vessels with multiple maintenance tasks, AI plans optimal routes for maintenance teams, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency.
Supply Chain Optimization and Logistics Management in the Maritime Industry
In the maritime industry, accurate demand forecasting is crucial for efficient capacity planning and resource allocation. AI algorithms, particularly machine learning models, have significantly enhanced these processes:
- Time Series Analysis: Advanced models like ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) and Prophet are employed to analyze historical shipping data and predict future demand patterns.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Techniques such as Random Forests, Gradient Boosting Machines, and Neural Networks are used to incorporate multiple variables (e.g., economic indicators, seasonal trends, geopolitical factors) into demand forecasts.
AI has transformed route optimization in the maritime industry, considering multiple factors to determine the most efficient shipping routes:
- Dynamic Weather Routing: AI algorithms process real-time meteorological data to optimize routes based on weather conditions, reducing fuel consumption and enhancing safety.
- Traffic Pattern Analysis: Machine learning models analyze historical AIS (Automatic Identification System) data to predict congestion in shipping lanes and optimize routes accordingly.
- Multi-Objective Optimization: AI systems balance multiple objectives such as fuel efficiency, time constraints, and environmental impact to determine optimal routes.
AI has also revolutionized container management and stowage planning, crucial aspects of maritime logistics:
- Automated Stowage Planning: AI algorithms optimize container placement on vessels, considering factors such as weight distribution, destination ports, and cargo type.
- Predictive Maintenance for Containers: Machine learning models analyze sensor data from smart containers to predict maintenance needs and prevent cargo damage.
- Real-Time Tracking and Visibility: AI-powered systems provide real-time visibility into container locations and conditions, enhancing supply chain transparency. CMA CGM, a leading container shipping company, uses an AI-powered stowage optimization system called TRAXENS, which has improved vessel utilization and reduced the risk of cargo damage.
AI plays also a crucial role in optimizing port operations, a critical node in the maritime supply chain.
- Berth Allocation: Machine learning algorithms optimize berth allocation based on vessel characteristics, cargo type, and port infrastructure.
- Yard Management: AI systems optimize container yard operations, reducing congestion and improving equipment utilization.
- Predictive Maintenance for Port Equipment: AI-driven predictive maintenance systems enhance the reliability of port equipment, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Enhanced Safety and Risk Mitigation in the Maritime Industry
As the maritime industry undergoes rapid digitalization, AI plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity.
- Network Traffic Analysis: AI algorithms monitor network traffic patterns to detect potential cyber threats or unauthorized access attempts.
- Behavioral Analysis: Machine learning models analyze user and system behaviors to identify anomalies that may indicate a security breach.
- Automated Threat Response: AI systems can automatically implement countermeasures in response to detected cyber threats, minimizing response times.
AI also enhances emergency response capabilities in the maritime industry:
- Incident Prediction: Machine learning models analyze historical incident data and current conditions to predict potential emergency scenarios.
- Resource Optimization: AI algorithms optimize the allocation of emergency resources based on incident severity and location.
- Decision Support Systems: AI-powered decision support systems provide real-time recommendations to crisis management teams during emergencies.
The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) utilizes AI-powered systems for maritime surveillance and emergency response coordination, enhancing their ability to detect and respond to incidents across European waters.
Crew Training and Performance Improvement in the Maritime Industry
One of the most impactful applications of AI in maritime crew training is the development of advanced simulation and virtual reality (VR) systems:
- Adaptive Learning Algorithms: AI-driven simulators can adjust scenario complexity based on a trainee's performance, ensuring optimal challenge levels and personalized learning experiences.
- Real-time Performance Analysis: Machine learning algorithms analyze trainee actions in simulated environments, providing instant feedback and identifying areas for improvement.
- Scenario Generation: AI can generate an infinite variety of realistic training scenarios, incorporating historical data on maritime incidents and near-misses to prepare crews for a wide range of potential situations.
- Performance Analytics: Deep learning models analyze trainee actions and decisions during simulations, providing detailed insights into areas for improvement.
AI is also transforming how crew performance is monitored and improved in real-time operations.
- Behavioral Analysis: Computer vision and machine learning algorithms can analyze crew behavior on the bridge, identifying potential safety risks or procedural non-compliance.
- Fatigue Detection: AI-powered systems can monitor signs of crew fatigue through facial recognition and behavioral analysis, alerting management to potential safety risks.
- Decision Support Systems: AI algorithms can provide real-time guidance to crew members during complex operations, enhancing decision-making and reducing human error.
AI in shipping is changing competency management in the maritime industry by creating tailored learning experiences.
- Skill Gap Analysis: Machine learning algorithms analyze individual performance data to identify skill gaps and recommend targeted training modules.
- Predictive Performance Modeling: AI systems can predict future performance based on historical data, allowing for proactive intervention and support.
- Continuous Assessment: AI-powered systems enable continuous evaluation of crew competencies, moving beyond traditional periodic assessments.
Port Density and Traffic Management in the Maritime Industry
One of the most impactful applications of AI in port operations is the optimization of berth allocation and vessel scheduling.
- Dynamic Berth Allocation Systems: AI algorithms analyze multiple factors such as vessel size, cargo type, handling equipment availability, and tidal conditions to optimize berth assignments. These systems can adapt in real time to changes in vessel arrivals or port conditions, maximizing berth utilization.
- Predictive ETA Modeling: Machine learning models leverage historical AIS (Automatic Identification System) data, weather patterns, and real-time vessel tracking to predict accurate arrival times. This enables ports to plan resources more effectively and reduce congestion.
AI in shipping applications includes how ports manage vessel and hinterland traffic:
- Adaptive Traffic Flow Optimization: AI algorithms analyze real-time data from various sources, including AIS, CCTV cameras, and IoT sensors, to optimize traffic flow within the port area. These systems can dynamically adjust traffic patterns to prevent bottlenecks and reduce congestion.
- Multimodal Transport Synchronization: AI-driven systems coordinate the movement of cargo across different transport modes (sea, road, rail) to minimize dwell times and optimize port throughput.
- Autonomous Vessel Traffic Services (VTS): AI-enhanced VTS systems can autonomously monitor and manage vessel movements, providing intelligent routing suggestions and collision avoidance alerts.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Marine Industry
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The integration of AI in the maritime industry has led to significant improvements in operational efficiency and productivity, revolutionizing various aspects of shipping operations.
Optimized Route Planning and Navigation Systems:
AI-powered navigation systems analyze real-time meteorological data, oceanographic conditions, and vessel traffic patterns to determine the most efficient routes. These systems utilize machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of data from sources such as satellite imagery, AIS (Automatic Identification System), and historical voyage records. The result is a dynamic route optimization in the vessel management software of autonomous vessels that adapts to changing conditions, reducing voyage times and enhancing overall fleet productivity.
AI-Enhanced Vessel Management Software:
Advanced vessel management software integrates AI capabilities to streamline shipboard operations. These systems use machine learning to analyze data from various onboard sensors and systems, providing real-time insights into vessel performance. AI algorithms can automatically adjust ship parameters, such as trim and ballast, to optimize performance based on current conditions.
Predictive Maintenance and Asset Management:
Digitalization in the maritime industry, with the help of machine learning algorithms, analyzes sensor data from shipboard equipment to predict potential failures before they occur. This predictive maintenance approach minimizes unscheduled downtime, improves vessel availability, and optimizes maintenance schedules. AI systems can also prioritize maintenance tasks based on criticality and resource availability.
Autonomous Vessel Operations:
While fully autonomous vessels are still in development, AI is enabling increasing levels of autonomy in ship operations. AI systems can handle navigation systems, collision avoidance, and engine management with minimal human intervention, potentially leading to more efficient and consistent vessel operations.
Reduced Operational Costs and Fuel Consumption
AI technologies are driving substantial cost reductions in maritime operations, particularly in fuel consumption and overall operational expenses.
Fuel Optimization Systems:
AI-powered fuel optimization systems analyze a multitude of factors, including vessel characteristics, load conditions, weather patterns, and engine performance, to minimize fuel consumption. This vessel management software uses complex machine learning models to continuously adjust engine settings, speed, and route to achieve optimal fuel efficiency.
Dynamic Trim Optimization:
AI systems continuously analyze vessel data to determine the optimal trim for current operating conditions. By maintaining the ideal trim, these systems significantly reduce hull resistance, leading to substantial fuel savings.
Intelligent Weather Routing:
AI-enhanced weather routing systems process vast amounts of meteorological and oceanographic data to determine the most fuel-efficient routes. These systems can predict and avoid adverse weather conditions, reducing fuel consumption and improving vessel safety.
Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization:
In the broader context of maritime logistics, AI is optimizing supply chain management, reducing operational costs associated with inventory, storage, and transportation. Machine learning algorithms forecast demand patterns, optimize inventory levels, and streamline intermodal connections.
Crew Resource Management:
AI-powered scheduling & allocation systems optimize crew deployments, reducing labor costs while ensuring compliance with work-rest regulations. These systems analyze factors such as crew qualifications, experience, & fatigue levels to create optimal rosters.
Improved Safety and Environmental Sustainability
The integration of AI in the maritime industry has significantly enhanced safety measures and environmental sustainability practices, revolutionizing traditional approaches to maritime operations.
Emissions Monitoring and Reduction:
AI in shipping plays a crucial role in monitoring and optimizing vessel emissions. Machine learning models analyze engine performance data, fuel consumption patterns, and operational parameters to optimize combustion processes and reduce emissions. These navigation systems can also ensure compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, such as IMO 2020.
Ballast Water Management:
AI-enhanced ballast water management systems optimize the treatment and exchange of ballast water, minimizing the spread of invasive species. Machine learning algorithms can predict optimal ballast water exchange points based on oceanographic data and vessel routes, ensuring compliance with international regulations.
Environmental Monitoring and Response:
AI-powered systems utilizing satellite imagery analysis and drone technology enhance the detection and response to environmental incidents such as oil spills. Machine learning algorithms can quickly analyze vast amounts of data to identify and track potential environmental hazards.
Advanced Collision Avoidance Systems:
As we talked about in AI's Application on the Maritime Industry, AI-powered navigation systems use sensor fusion technology to make a full picture of the situation by combining data from radar, AIS (Automatic Identification System), LIDAR, and high-resolution cameras. ML algorithms process this data in real-time, predicting potential collision scenarios and recommending evasive maneuvers. These systems are particularly crucial in congested waterways and adverse weather conditions.
Enhanced Decision-Making and Risk Management
The incorporation of AI in vessel management software and logistics systems has dramatically improved decision-making processes and risk management strategies in the maritime industry.
Route Optimization:
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data, real-time weather conditions, ocean currents, and port congestion to suggest optimal routes. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also enhances safety by avoiding potentially hazardous/dangerous areas.
Cargo Management:
AI algorithms optimize cargo loading and unloading processes, considering factors such as vessel stability, weight distribution, and port logistics. This improves operational efficiency and reduces the risk of accidents during cargo handling.
Dynamic Risk Modeling:
Machine learning models analyze vast datasets encompassing historical incidents, near-misses, and current operational parameters to create dynamic risk profiles for each voyage. This allows for real-time risk assessment and mitigation strategies due to digitalization in the maritime industry.
Cybersecurity Enhancement:
As vessels become more connected, AI plays a crucial role in detecting and preventing cyber threats. AI-powered systems can identify anomalies in network traffic and automatically implement countermeasures to protect critical ship systems.
New Business Models and Opportunities
The integration of AI in the maritime industry is not only enhancing existing processes but also catalyzing the emergence of innovative business models and creating new opportunities across the sector. This transformation is changing the scene of shipping, logistics, and maritime services:
- Autonomous Vessel Operations: The development of autonomous and semi-autonomous vessels represents a paradigm shift in the maritime industry. AI-powered systems capable of handling navigation, collision avoidance, and engine management with minimal human intervention are paving the way for new operational models:
- Remote Operations Centers: Centralized facilities where AI-assisted human operators can monitor and control multiple autonomous vessels simultaneously.
- Unmanned Short-Sea Shipping: AI-driven autonomous vessels optimized for coastal and inland waterway transport, potentially reducing operational costs and increasing route flexibility.
- Hybrid Crewing Models: Combining AI systems with reduced human crew for enhanced efficiency and safety in long-haul voyages.
Real-life example: Yara Birkeland, developed by Kongsberg Maritime and YARA International, is set to be the world's first fully autonomous and zero-emission container ship, utilizing AI for navigation and operations.
AI-as-a-Service in Maritime Operations
The proliferation of AI technologies is giving rise to specialized service providers offering AI solutions tailored to the maritime industry:
- Predictive Maintenance Services: Companies that offer AI-powered predictive maintenance as a service utilize advanced analytics to optimize vessel performance and reduce downtime.
- Route Optimization Platforms: Cloud-based services providing AI-driven route optimization, considering factors such as weather, fuel efficiency, and port congestion.
- Dynamic Pricing Models: AI-powered platforms offering real-time freight rate optimization and market analysis services.
Blockchain-AI Integration in Maritime Logistics
The combination of AI and blockchain technology is enabling new models for secure, transparent, and efficient maritime documentation and cargo tracking:
- Smart Contracts for Shipping: AI-powered systems automating contract execution and payment processes based on predefined conditions and real-time data.
- Enhanced Logistics and Supply Chain Management Visibility: AI algorithms analyzing blockchain data to provide predictive insights and optimize supply chain operations.
- Automated Customs Clearance: AI systems process documentation and assess risk profiles to expedite customs procedures.
Key Technologies Powering AI in the Marine Industry
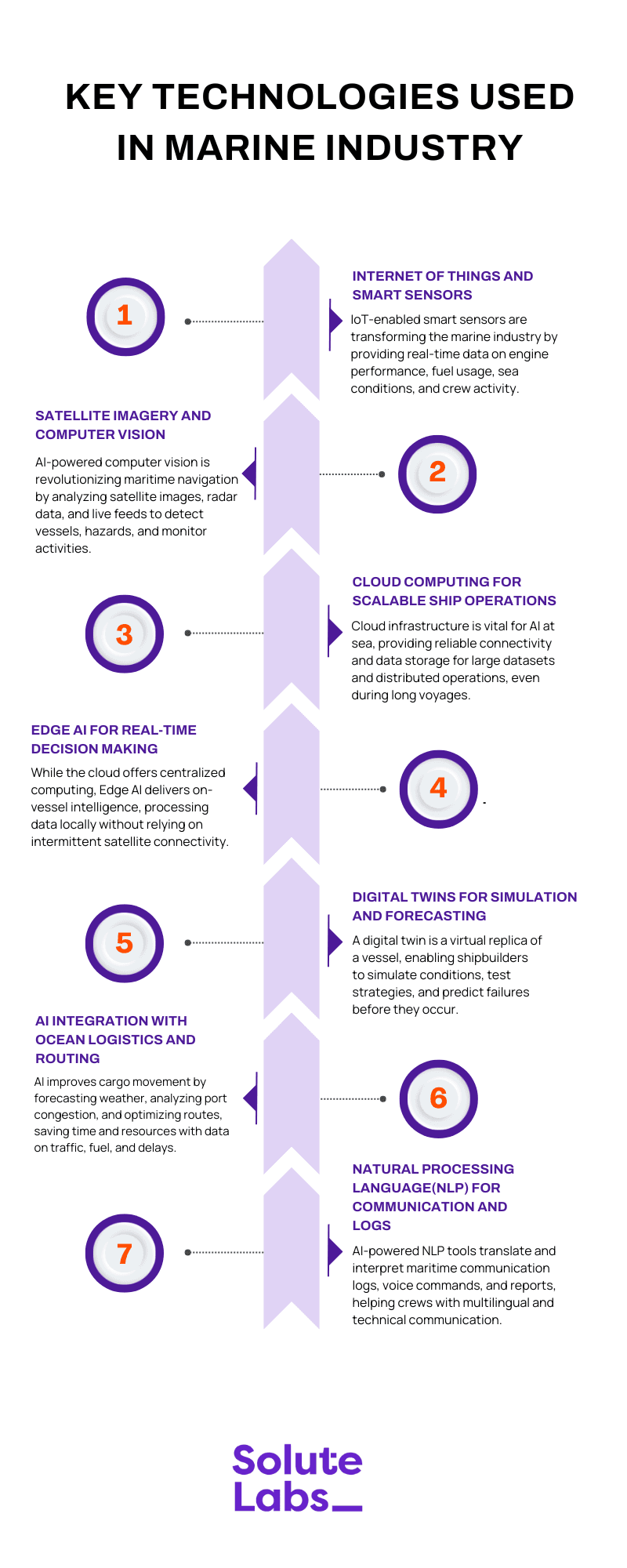
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into the marine industry isn’t just a technological upgrade; it’s a complete shift in how operations at sea are planned, executed, and optimized. From autonomous navigation to smarter crew allocation, the backbone of AI’s growing influence lies in the latest technologies that enable it. Below are the core technological pillars that are shaping the future of maritime innovation.
1. Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Sensors
One of the most important developments in intelligent systems is the ability to collect data. In the marine industry, IoT-enabled smart sensors are revolutionizing real-time monitoring. Installed across ships, ports, and cargo systems, these sensors gather vital data on engine performance, fuel usage, sea conditions, structural integrity, and even crew activity.
For instance, during rough sea transits, sensors can detect early signs of wear and tear, triggering alerts before minor issues escalate. This constant stream of information is essential for AI systems to make informed decisions. IoT acts as the sensory nervous system of maritime AI, ensuring that decisions are not based on guesswork but on precise, up-to-the-minute data.
2. Satellite Imagery and Computer Vision
The use of AI-powered computer vision systems has become a game-changer for maritime navigation and security. These systems analyze satellite images, live camera feeds, and radar data to identify vessels, monitor coastline activities, and detect potential hazards in shipping routes.
Advanced image recognition tools enable early detection of piracy attempts, illegal fishing, or even marine pollution. Combined with machine learning algorithms, these vision systems continuously improve their accuracy, helping crews and autonomous systems make safer navigation choices in real time. They are particularly useful in remote or under-monitored regions where traditional radar systems fall short.
3. Cloud Computing for Scalable Ship Operations
Cloud infrastructure plays a pivotal role in powering AI tools at sea, especially when dealing with large datasets and distributed operations. With vessels often at sea for extended periods, reliable connectivity and data storage are critical.
Modern ship management & maintenance platform optimization with the cloud allows fleets to centralize their performance data, coordinate repairs, and monitor health diagnostics across various ship components. The cloud also enables secure remote updates, predictive maintenance scheduling, and shared access to logs across geographies. As a result, downtime is minimized and fleet productivity is maximized, all without physically being present on the vessel.
4. Edge AI for Real-Time Decision Making
While the cloud provides powerful centralized computing, Edge AI brings intelligence directly to the vessel. These compact yet powerful systems are deployed on ships to process data locally, without relying heavily on intermittent satellite connectivity.
Imagine an autonomous ship facing unpredictable weather. Edge AI systems can instantly analyze onboard sensor data, adjust course or speed, and activate emergency protocols if needed. This local decision-making capability is essential when every second counts. It also supports cost-effective operations by reducing the need for constant data transmission to shore-based servers.
5. Digital Twins for Simulation and Forecasting
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset or system, and it’s becoming an essential tool in marine AI applications. By modeling the entire structure and behavior of a vessel, shipbuilders and operators can simulate conditions, test strategies, and predict failures long before they happen.
This technology is particularly beneficial for maritime training AI environments. Trainees can interact with hyper-realistic ship scenarios in simulated environments, making decisions under pressure without any real-world risks. Over time, training models evolve using feedback from actual performance data, creating a continuous improvement loop between simulation and real-world learning.
6. AI Integration with Ocean Logistics and Routing
Efficient cargo movement depends on smart planning and execution. AI’s ability to forecast weather patterns, analyze port congestion, and optimize routes is drastically improving shipping efficiency. When AI algorithms are fed with traffic data, fuel consumption records, and historical delays, they can plan routes that save both time and resources.
This is where ocean logistics AI makes a significant impact. By orchestrating end-to-end supply chains, from the factory to the final port, AI can reduce dwell times, ensure proper load balancing, and anticipate customs clearance delays. The result is a smarter, leaner logistics framework with fewer bottlenecks and enhanced delivery accuracy.
7. Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Communication and Logs
Communication on ships involves various languages, codes, and highly technical terminologies. AI-powered NLP tools are being used to interpret, summarize, and even translate maritime communication logs and reports. These systems also help with voice command interpretation in bridge systems and smart assistance tools for crews.
Additionally, NLP can auto-generate incident reports or maintenance logs, reducing manual paperwork and allowing officers to focus more on operational responsibilities. Over time, AI can identify recurring issues in log data and suggest proactive steps for resolution.
Future of AI in the Marine Industry | Final Thought
As we sail into the future, the waves of innovation driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are set to change the marine industry in ways we can only begin to imagine. From autonomous vessels cruising the high seas to intelligent navigation systems that adapt to real-time conditions, AI is not just a tool anymore—it's becoming the compass guiding the maritime sector toward uncharted territories of efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
At Solutelabs, we specialize in crafting custom AI and machine learning solutions that help you grow your maritime businesses to navigate the complexities of the digital age. Let us be your compass, guiding you toward a future where AI isn't just a distant dream but a driving force behind your success.
Don't let your business get lost at sea in the AI revolution. Contact Solutelabs today and let's chart a course towards a brighter, AI-powered future. After all, in the maritime industry, it's all about staying 'a-head' of the curve! (Sorry, not sorry for so many puns).
